Database - An Overview
A database management system (DBMS) enables you to organize data so that they can be easily stored, accessed, modified, and maintained. Data are essentially facts. They may include text, numbers, sounds, and objects (graphic images). A database is a collection of related data. Data within a database are arranged into fields and records. A field is a single piece of data (for example a customer name). A record is a group of related fields - a customer's record may include fields for a customer's name, address, and telephone number. In Access, data are stored in a single table or in a collection of related tables. A table displays data in columnar (column and row) form. Each row represents a single record, and each column, a specific field. The intersection of a column and row is referred to as a cell.
Before you can use Access to store data, you must first create a database file. You can then store data in the database file within a table or collection of tables. As described earlier, a table is a storage container that displays data in columnar (column and row) form. Each row represents a single record (a group of related fields), and each column, a specific field (a single piece of data). The intersection of a column and row is referred to as a cell. Data can be queried (located based on a set of criteria), analyzed, reorganized, presented in a report, or printed.
In an Access database file, data are stored in a table or tables. Tables display records in a database. You can, therefore, examine or edit many records at once. You can also add records to and remove them from the table. A single database file can hold and store multiple tables. You can develop tables to contain different types of information. For example, a retail business may have different tables that contain data for its customers, vendors, employees, and products.
A query is a search that lists records from a database based on criteria that you specify. You may also present data in a report, a more formal user-defined presentation of records.
Whenever you create or open a database file, the Database window appears in Access's work area. It acts as a GUI (Graphical User Interface) menu system for objects - items stored in the database file. Objects include tables, queries, forms, reports, macros, and modules.
The Database window displays a tab for each object type. Each object you create will be listed as an icon within the screen associated with its respective tab. For example, soon you will create a table named Customer List. After you create it, its icon will appear within the Tables tab of the Database window. Each tab also has command buttons for creating a new object (New button), retrieving, displaying, or executing an object (Open, Preview, or Run button), and editing an object (Design button).
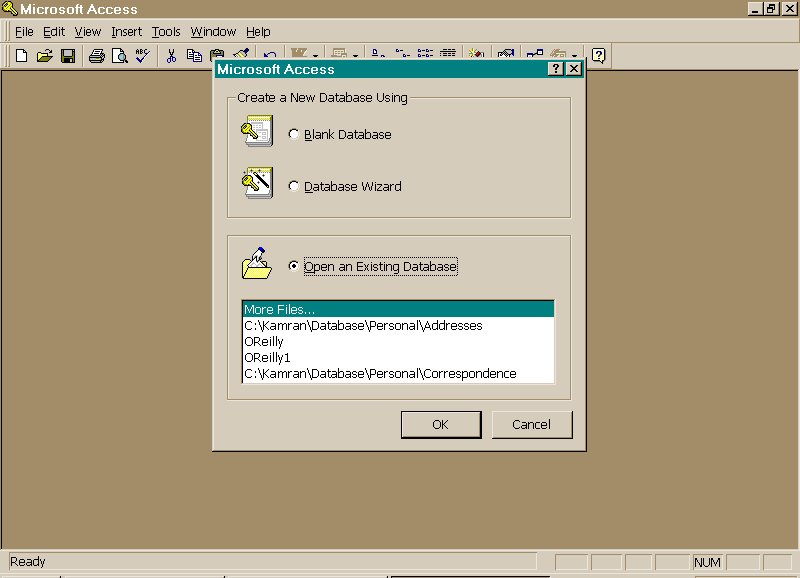
Access's online help feature includes general and specific help windows, a search feature, examples, demos, and reference information. Most dialog boxes also have a Help button that accesses a Help window related to their operation. The following figure shows you what the Access window looks like when you first open the Access program.

|
Continue… Next page |
Top of the page |
Opening Page |